PostgreSQL offers a built-in array function named ARRAY_TO_STRING() that accepts an array, converts it into strings, and concatenates the strings using a delimiter/separator. The separator can be any value, such as white space, comma, semi-colon, etc.
This write-up will teach you how to use the ARRAY_TO_STRING() function in Postgres via suitable examples. So, let’s start!
How to Use ARRAY_TO_STRING() Function in Postgres?
In Postgres, the below-mentioned syntax is used for the ARRAY_TO_STRING() function:
ARRAY_TO_STRING(arr, sep[, text]);
In the above syntax:
- “arr” represents an array to be converted to strings.
- “sep” represents a separator/delimiter that will be used between the strings.
- “text” is an optional parameter that replaces the NULL values with the specified text.
The return type of the ARRAY_TO_STRING() function will be TEXT.
Example 1: How to Use ARRAY_TO_STRING() Function in Postgres?
Let’s learn the working of the ARRAY_TO_STRING() function using the below code:
SELECT ARRAY_TO_STRING( ARRAY[1, 23, 150, -1, 2, -3, -1, 12, 121], ',', '0' );
In this example:
- An array is passed as the first argument.
- A comma is passed as a separator.
- And “0” is passed as the third parameter that will replace the NULL value(if any) with the 0.
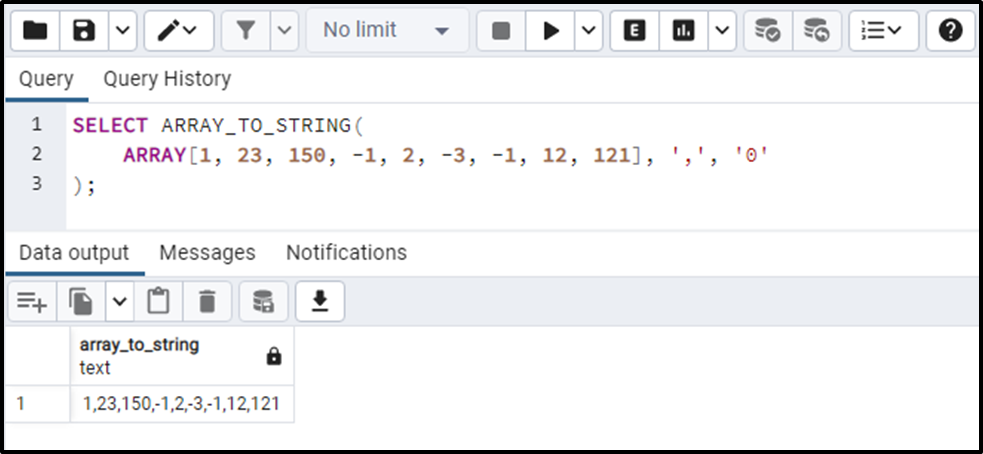
The output snippet proves that the given array has been converted into a string, and a comma is concatenated with each array element.
Example 2: How Does the ARRAY_TO_STRING() Function Deals With the Null Values in Postgres?
In the below-given input array, there are some NULL values. We will pass “0” as the third parameter to the ARRAY_TO_STRING() function. Consequently, it will replace the NULL value(if any) with 0:
SELECT ARRAY_TO_STRING( ARRAY[1, 23, NULL, -1, 2, NULL, -1, NULL, 121], ',', '0' );
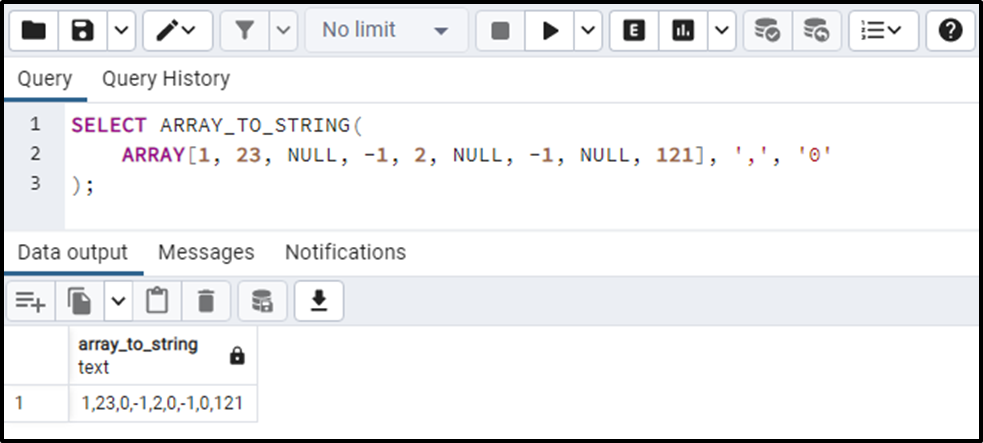
The output shows that the NULL values have been replaced with the specified null_text, i.e., “0”.
Example 3: How to Use ARRAY_TO_STRING() Function on Table’s Data in Postgres?
We have created a table named “st_information” that contains the following data:
SELECT * FROM st_information;
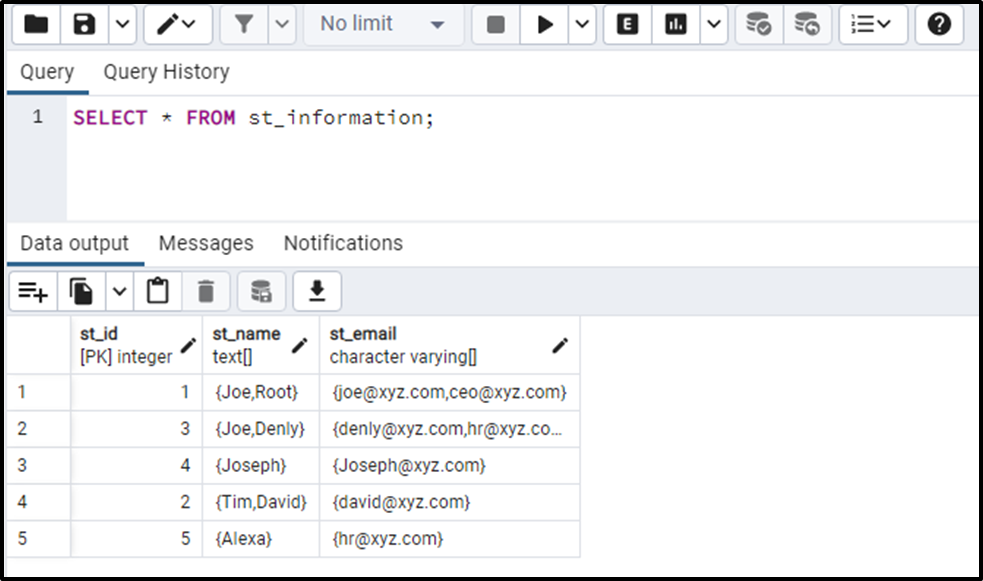
Let’s use the ARRAY_TO_STRING() function on “st_name” array to convert it into a string:
SELECT ARRAY_TO_STRING(st_name, ':', '-') FROM st_information;
In the above example code:
- An array-type column is passed as the first argument to the ARRAY_TO_STRING() function.
- A colon is passed as a separator/delimiter.
- “-” is passed as the third parameter that will replace the NULL value(if any) with “-”.
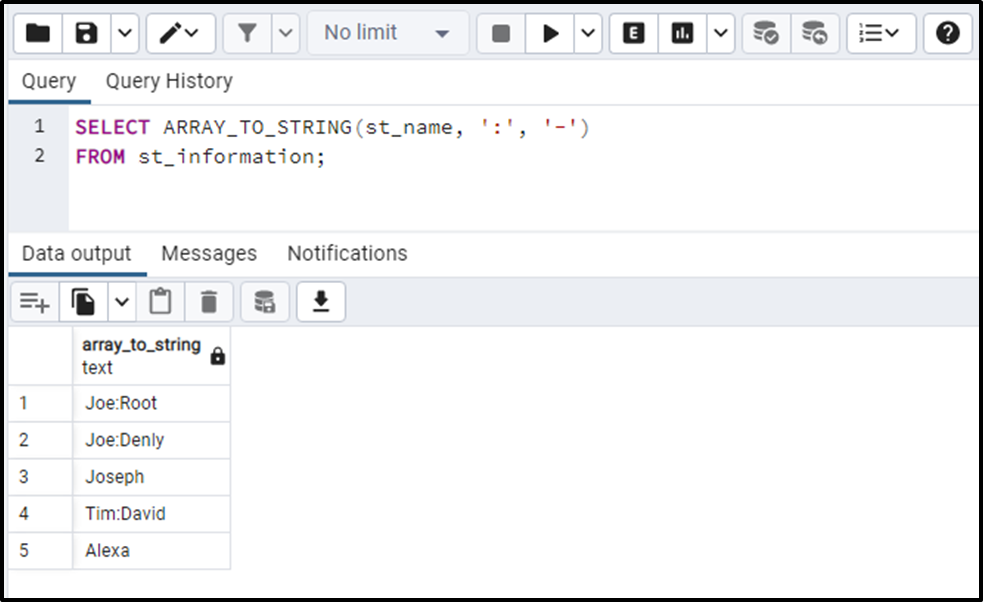
The output clarifies that the input array has been converted into a string.
That’s it from this Postgres tutorial!
Conclusion
PostgreSQL offers a built-in array function named ARRAY_TO_STRING() that accepts three arguments: an array, a delimiter/separator, and a text to replace the null values. The ARRAY_TO_STRING() function converts the given array into strings and concatenates the strings using a delimiter/separator. The return type of the ARRAY_TO_STRING() function is TEXT. Postgres ARRAY_TO_STRING() function is explained with practical examples in this write-up.



