In PostgreSQL, SERIAL is a pseudo-type that generates an auto-incrementing column. If you specify SERIAL as the data type for a column during table creation, PostgreSQL will automatically generate unique values for that particular column. However, occasionally users may need to override the default behavior of a SERIAL column. For this purpose, users must explicitly provide the column names and their corresponding values in the INSERT statement.
This post demonstrates how to override a SERIAL column in PostgreSQL using suitable examples.
Can a User Override a SERIAL Column in PostgreSQL?
Yes! A SERIAL column can be overridden by the user. This can be done by explicitly specifying the name of the SERIAL column in the INSERT statement and providing a corresponding value for that particular column.
Consider the following steps for a profound understanding of overriding the SERIAL column:
Step 1: Create a SERIAL Column
Let’s first create a SERIAL column. For this purpose, specify the “SERIAL” data type for a specific column at the time of table creation:
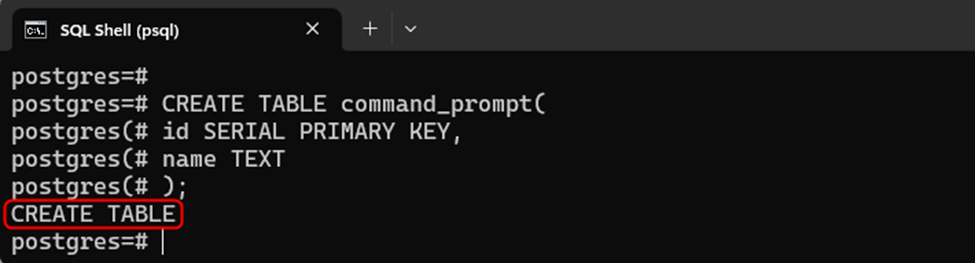
CREATE TABLE command_prompt( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT );
A table named “command_prompt” with a SERIAL data type has been successfully created:
Step 2: INSERT Data
Now insert a couple of records in the command_prompt table by executing the following query:
INSERT INTO command_prompt(name)
VALUES ('blog 1'),
('blog 2'),
('blog 3')
RETURNING *;The “RETURNING *” clause is used in the above query to get the newly inserted records:
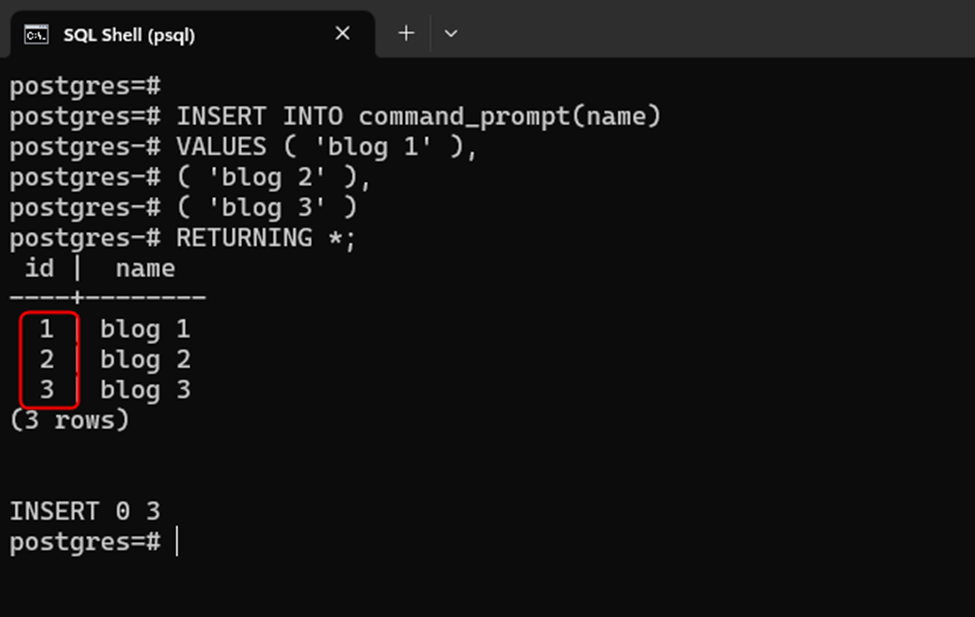
From the above output snippet, you can observe that the id column is filled automatically with the sequence of unique values.
Step 3: Override the SERIAL Column
Use the INSERT command, and explicitly specify the id column in it to override the SERIAL column:
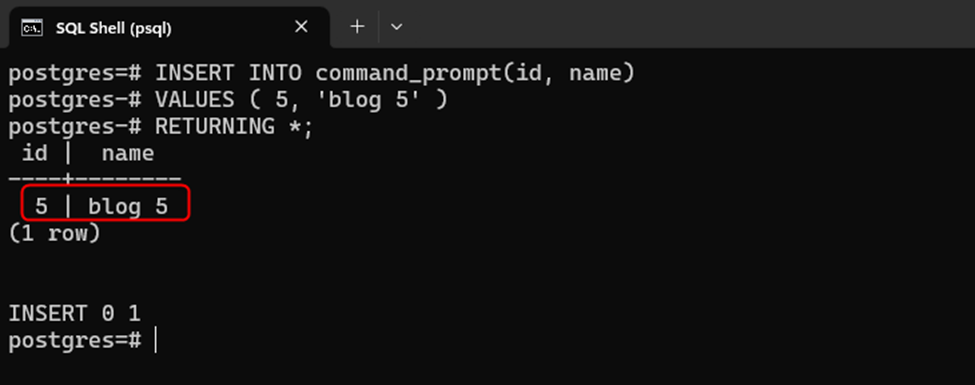
INSERT INTO command_prompt(id, name) VALUES (5, 'blog 5') RETURNING *;
The following snippet demonstrates that the SERIAL column has been successfully overridden:
Let’s insert one more record in the “command_prompt” table for a profound understanding of the SERIAL column:
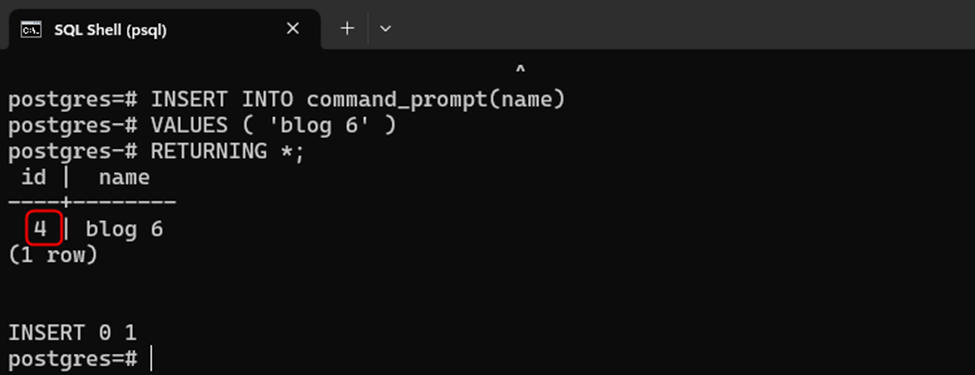
INSERT INTO command_prompt(name)
VALUES ('blog 6')
RETURNING *;It is clear from the output that when a new record is inserted, the auto-incrementing sequence of the serial column starts from where it left off:
That’s all about overriding a SERIAL column in PostgreSQL.
Conclusion
Yes! A SERIAL column can be overridden by the user by explicitly specifying the name of the column in the INSERT statement and providing a corresponding value for that particular column. Overriding a SERIAL column allows us to specify a value of our choice instead of letting it automatically increase on its own. This write-up has demonstrated a complete guide on overriding a SERIAL column in PostgreSQL.



