A schema in database management systems represents a set of rules that regulate/handle a database. It is a logical structure that holds various database objects like views, tables, indexes, sequences, etc. In Postgres, “public” is a Default schema. So, by default, Postgres users can access the "public" schema and create objects in it, such as views, tables, etc.
The SET SEARCH_PATH command, however, allows a user to set any other schema as the default schema. This post demonstrates how to change a schema in Postgres using the methods described below:
- Method 1: Change Schema for User’s Current Session
- Method 2: Change the Default Schema Permanently
Method 1: Change Schema for User’s Current Session
This section presents stepwise instructions to change the schema for the current session only:
Step 1: Check the Current/Default Schema
Execute the below-provided command to check the current/default schema:
SHOW SEARCH_PATH;
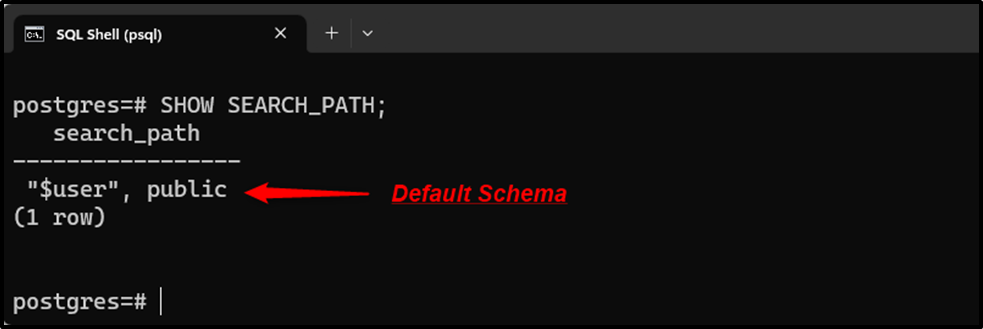
The above snippet shows that the default schema is “public”.
Step 2: Change the Default Schema
Now run the “\dn” command to see available schemas:
\dn
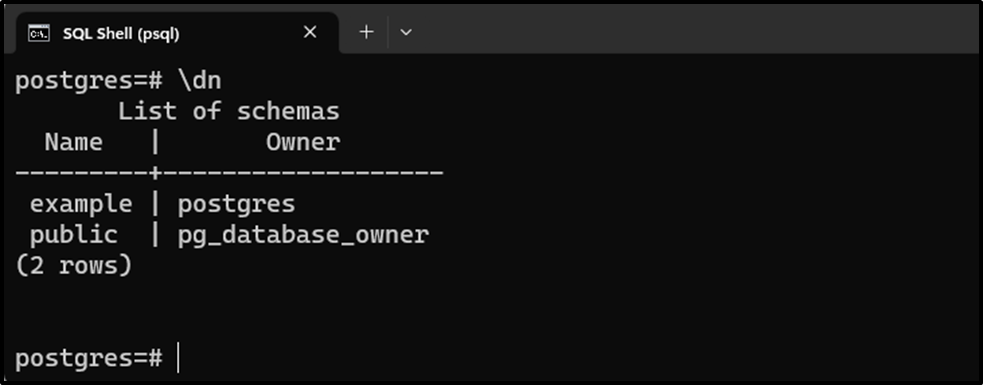
Suppose we want to set the “example” schema as the default schema. For this purpose, use the “SET SEARCH_PATH” command, as follows:
SET SEARCH_PATH = example;
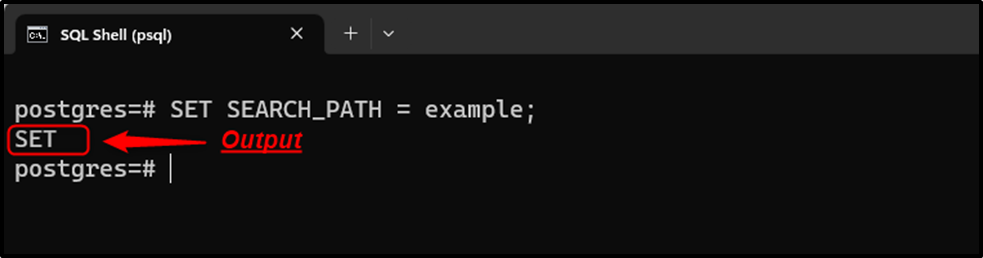
The “SET” message in the output indicates that the selected schema has been set as the default schema.
Step 3: Confirm the Current Schema
You can verify the default schema for the current session, using the below-provided command:
SHOW SEARCH_PATH;
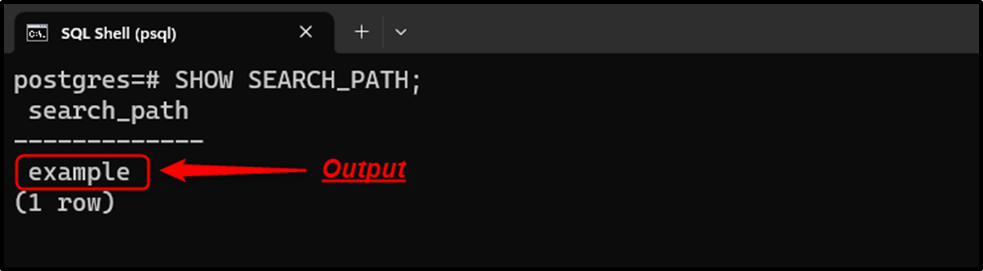
The “example” schema has been set as the default schema. However, it will remain the default schema for the current session only. Once the current session expires, the default schema will be reset to the “public” schema.
Method 2: Change the Default Schema Permanently
This section describes the following aspects of changing the default schema permanently:
- Changing the Schema at Database Level
- Changing the Schema at the User Level
How to Change Default Schema Permanently at the Database Level?
To change a default schema at the database level, the “ALTER DATABASE” command is used with the “SET SEARCH_PATH” clause:
ALTER DATABASE db_name SET search_path TO schema_name;
Replace the “db_name” and “schema_name” with the database and schema name of your choice.
Step 1: Connect to the Database
First, use the “\l” command to see the available databases:
\l
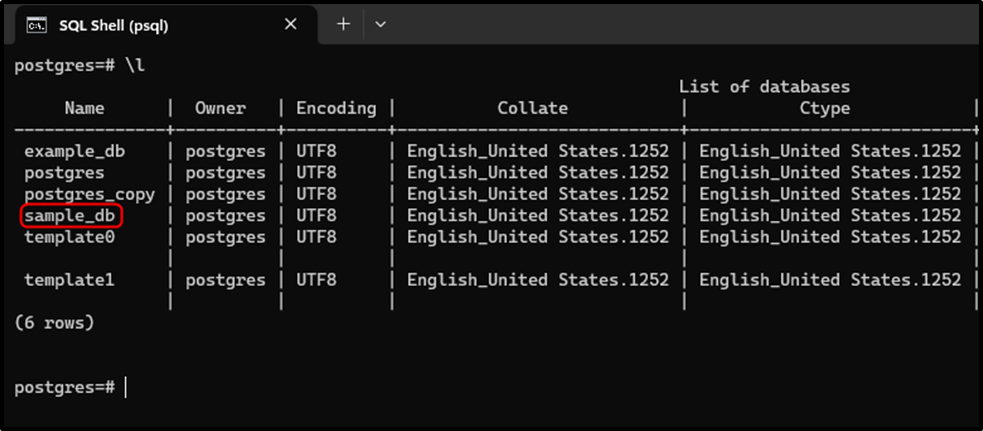
Let’s establish a connection to a database named “sample_db”:
\c sample_db;
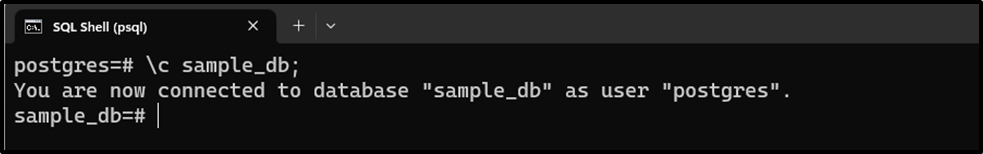
Step 2: Check the Current Schema
Execute the below-provided command to check the current/default schema for the selected database:
SHOW SEARCH_PATH;
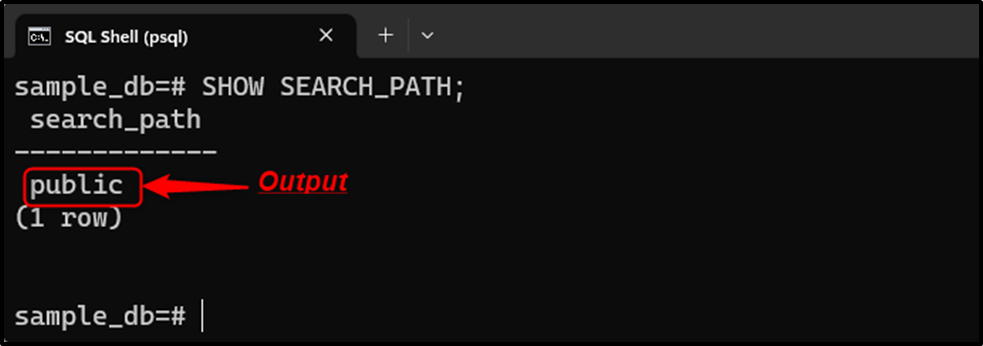
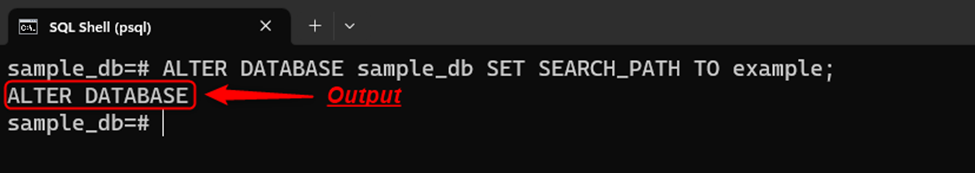
To change the “public” schema to the “example” schema at the database level, the “ALTER DATABASE” command will be used as follows:
ALTER DATABASE sample_db SET SEARCH_PATH TO example;
Step 3: Confirm the Current Schema
You can check the current schema using the below-provided command:
SHOW SEARCH_PATH;
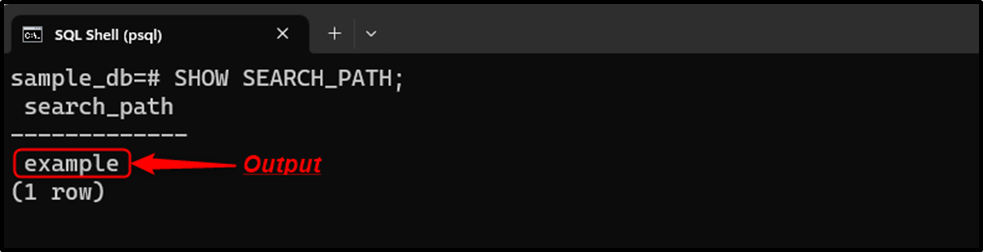
Now, whenever you establish a connection with the “sample_db” database, the default schema for that particular database would be “example”.
How to Change Default Schema Permanently at User Level?
To change a default schema at the user/role level, the “ALTER USER” or “ALTER ROLE” command is used with the “SET SEARCH_PATH” clause:
ALTER ROLE|USER role_name SET search_path TO schema_name;
Specify the user name and schema name of your choice in place of “role_name” and “schema_name”.
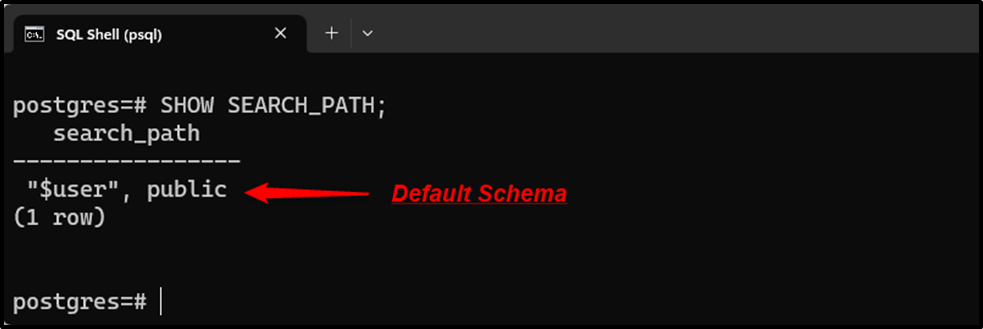
Step 1: Current Default Schema
We are currently logged in as the “postgres” user whose default schema is “public”, as shown in the following snippet:
Step 2: Change the Default Schema Permanently at the User Level
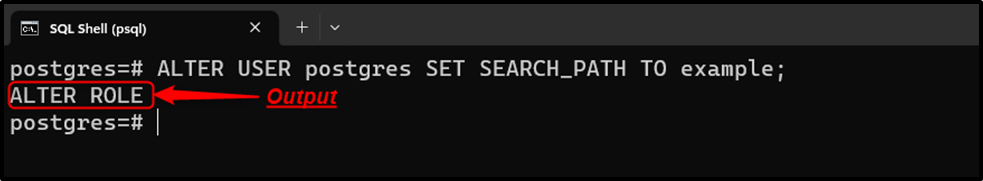
To change the “public” schema to the “example” schema at a user level, the “ALTER USER” command will be used as follows:
ALTER USER postgres SET SEARCH_PATH TO example;
Step 3: Confirm the Current Schema
To verify the current schema, use the below-provided command:
SHOW SEARCH_PATH;
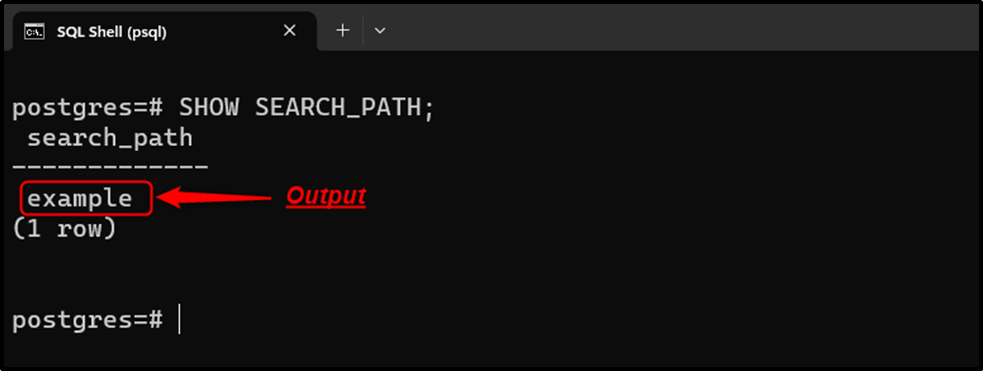
Now, whenever you logged in as a “postgres” user, the default schema would be “example”.
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, the “SET SEARCH_PATH” command is used to change a schema temporarily. To change a schema permanently at the database level or user lever, the “ALTER DATABASE” and "ALTER USER" commands are used with the “SET SEARCH_PATH” command, respectively. This post presented a step-by-step guide on how to change the default schema in Postgres.



