"JavaScript Object Notation", popularly known as JSON is a process of storing data in “key-value” pairs format. JSON is easy for humans to read/understand and is generally utilized for communication between servers and clients. Postgres offers many useful functions and operators to work with JSON data, such as TO_JSON(), ROW_TO_JSON(), ARRAY_TO_JSON, and many more.
This write-up will guide you on using the ROW_TO_JSON() function in PostgreSQL using practical examples.
How Does the ROW_TO_JSON() Function Work in PostgreSQL?
ROW_TO_JSON() is a built-in JSON function that accepts any valid SQL composite type value and converts it into a JSON object.
Syntax
Below is the PostgreSQL ROW_TO_JSON() function's syntax:
ROW_TO_JSON(row RECORD, pretty BOOLEAN);
Parameters
The “row” is a mandatory parameter that must be a value of type composite. While “pretty” is an optional parameter that beautifies the retrieved result of the ROW_TO_JSON() function.
Let’s implement this function practically!
Example 1: Using ROW_TO_JSON() on Composite Types
The following example illustrates the use of the ROW_TO_JSON() function on composite type values :
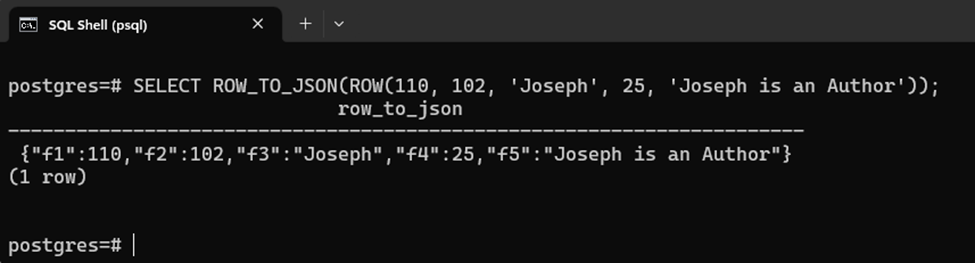
SELECT ROW_TO_JSON(ROW(110, 102, 'Joseph', 25, 'Joseph is an Author'));
Here in the above code:
- We utilized the “ROW” expression to construct a composite type.
- The composite type value contains five elements.
- After that, the ROW_TO_JSON() is utilized on the composite type data.
- The ROW_TO_JSON() function auto-generates keys for the JSON object in “fn” format, where “n = 1, 2, 3, …”.
The output shows that the composite type has been successfully converted into a JSON object:
Example 2: Using ROW_TO_JSON() With pretty Parameter
Pass the Boolean “true” as a pretty argument to beautify the converted JSON object:
SELECT ROW_TO_JSON(ROW(110, 102, 'Joseph', 25, 'Joseph is an Author'), true);
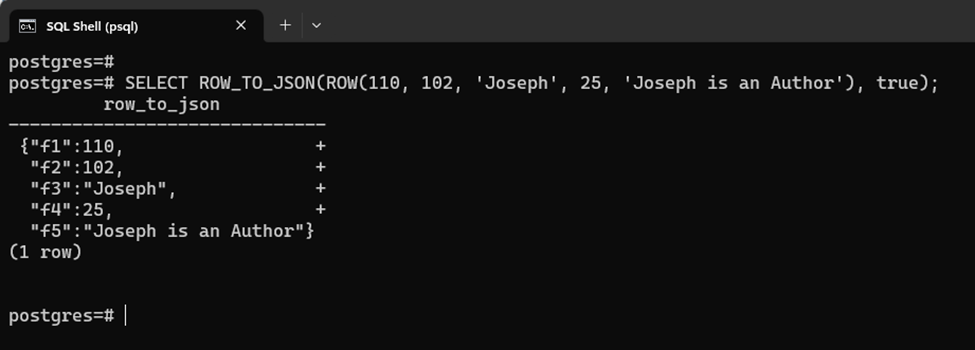
That’s all about converting any SQL value to JSON Object.
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, the ROW_TO_JSON() is a built-in JSON function that accepts any valid SQL composite type value and converts it into a JSON object. To use ROW_TO_JSON() in Postgres, use the “ROW_TO_JSON(row RECORD, pretty BOOLEAN);” syntax. Where the “row” is a mandatory parameter that must be a value of type composite. While “pretty” is an optional parameter that beautifies the retrieved result of the ROW_TO_JSON() function. This post has demonstrated a practical guide on different use cases of the ROW_TO_JSON() function in Postgres.



