The primary keys are widely used in all relational databases, including Postgres. Developers prefer to create every table with a primary key. The primary keys in Postgres are used to identify a record uniquely. You can create a primary key for any data type; however, most frequently, the primary keys are defined using the INT data type. In such cases, the user specified a unique value for each primary key while inserting the data into a table.
In Postgres, a pseudo data type named “SERIAL” can be used for the PRIMARY KEY column to define an auto-incremented primary key.
This write-up will teach you how to define an auto-incremented primary key in Postgres via practical examples.
How to Define/Create an Auto Incremented Primary Key in Postgres?
You can define an auto-increment primary key at the time of table creation using the following syntax:
CREATE TABLE table_name( col_name SERIAL PRIMARY KEY )
An auto-incremented unique identifier will be created using the syntax above.
Example: How Do I Create/Define an Auto-Incremented Primary Key in Postgres?
This example will show you how to define an auto-incremented primary key while table creation:
CREATE TABLE company_details( c_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, c_ceo TEXT, ceo_id INT );
The above query will create an auto-incremented PRIMARY KEY named “c_id” for the company_details table:
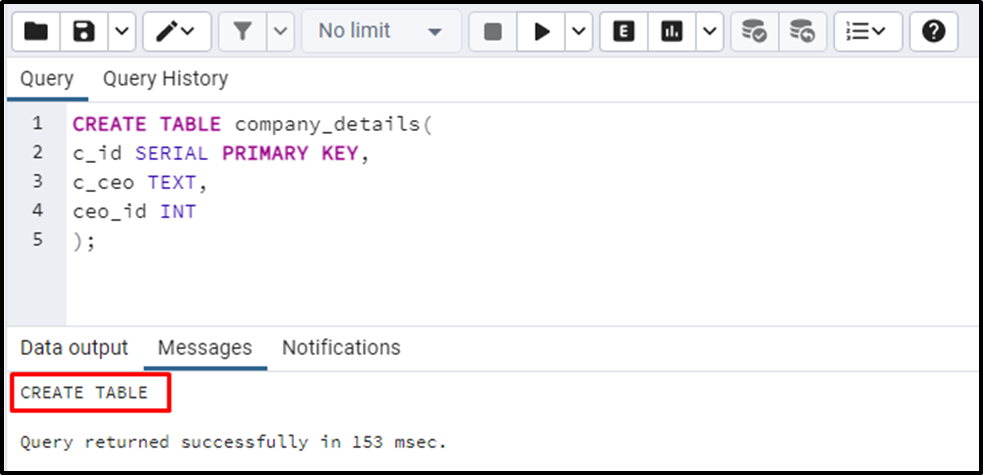
The above snippet shows that a table named “company_details” has been created with three columns: c_id, c_ceo, and ceo_id. Now, we will execute the INSERT INTO statement to insert the data into the “company_details” table:
INSERT INTO company_details(c_ceo, ceo_id)
VALUES ('Joe', 5),
('Joseph', 2),
('Alex', 3),
('Ambrose', 1),
('Mike', 4),
('Seth', 6);Since the c_id column is defined with the SERIAL data type, so there is no need to specify the value for that particular column while data insertion. The value of the c_id column will be auto-incremented for each record:
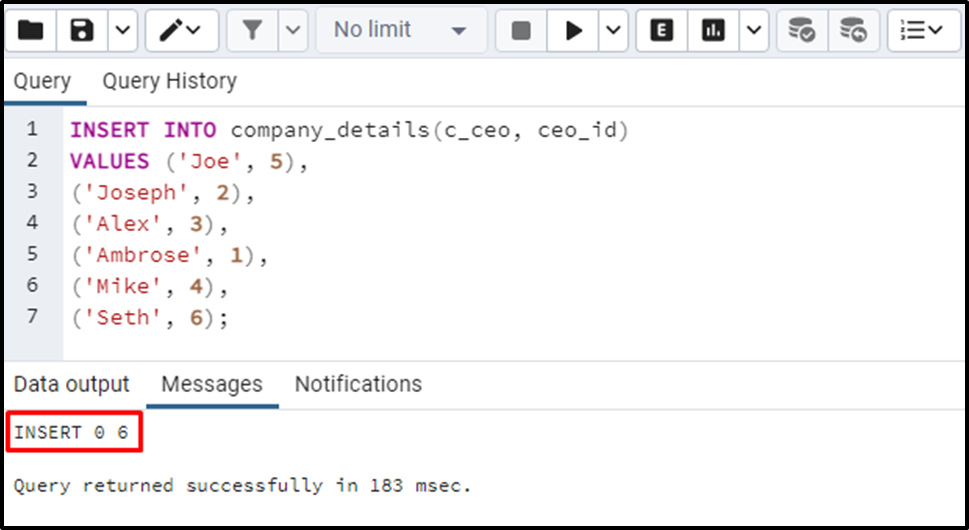
All the records have been inserted into the company_details table. Executing the SELECT * command will show the table’s data:
SELECT * FROM company_details;
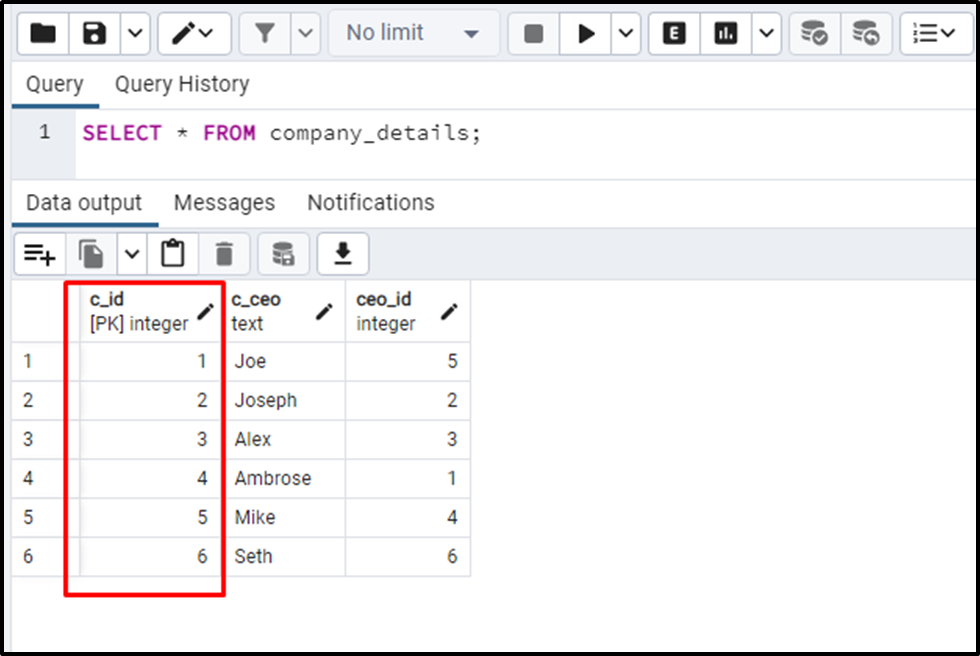
The output snippet authenticates the working of the auto-incremented primary key.
This is how you can create an auto-incremented Primary key in Postgres.
Conclusion
To define an auto-incremented primary key in Postgres, specify a column name followed by a pseudo data type named “SERIAL”, and then specify the PRIMARY KEY keyword. In such cases, PostgreSQL will address all behind the scene complexities and auto-increment the primary key value for each insertion. This write-up explained how to define/create an auto-incremented primary in Postgres using the SERIAL pseudo-data type.



