In PostgreSQL, a LIMIT clause allows us to get/fetch the top n rows. The LIMIT clause allows us to extract a subset of rows from a resultant table returned by a query. LIMIT is an optional clause in Postgres; however, if we have to fetch the first N rows, then the LIMIT clause must be used.
This post will explain how to get the first N rows in PostgreSQL through practical examples. So, let’s begin.
How to Get/Fetch Top N Rows in Postgres?
As the name suggests, the LIMIT clause is used to fetch limited records from a result set. The below snippet demonstrates the basic syntax of the LIMIT clause:
SELECT col_list FROM tab_name ORDER BY ASC | DESC LIMIT no_of_rows;
Let’s comprehend the above syntax stepwise:
- col_list represents a single or multiple columns to be selected.
- tab_name represents a table from which the data will be fetched.
- ORDER BY is an optional clause that sorts the table’s records in a particular order.
- The LIMIT clause determines how many rows to fetch.
Example #1: How to Fetch Top Five Rows of a Table in Postgres?
We have a table named “article_details” that consists of three columns: article_id, article_title, and published_date. Let’s run the SELECT statement to fetch the table’s data:
SELECT * FROM article_details;
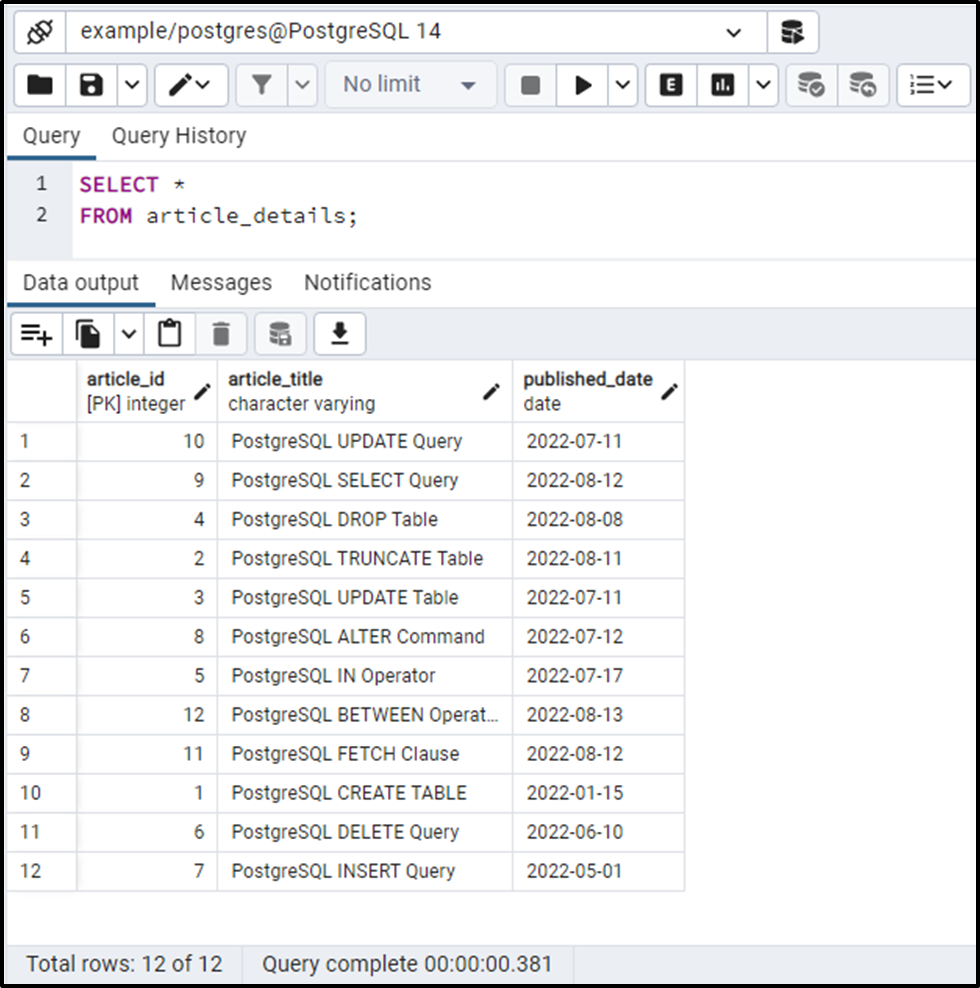
The article_details table has twelve unsorted records. Suppose we want to get the top five articles regarding their ids. To achieve this, let’s run the below query:
SELECT * FROM article_detail ORDER BY article_id ASC LIMIT 5;
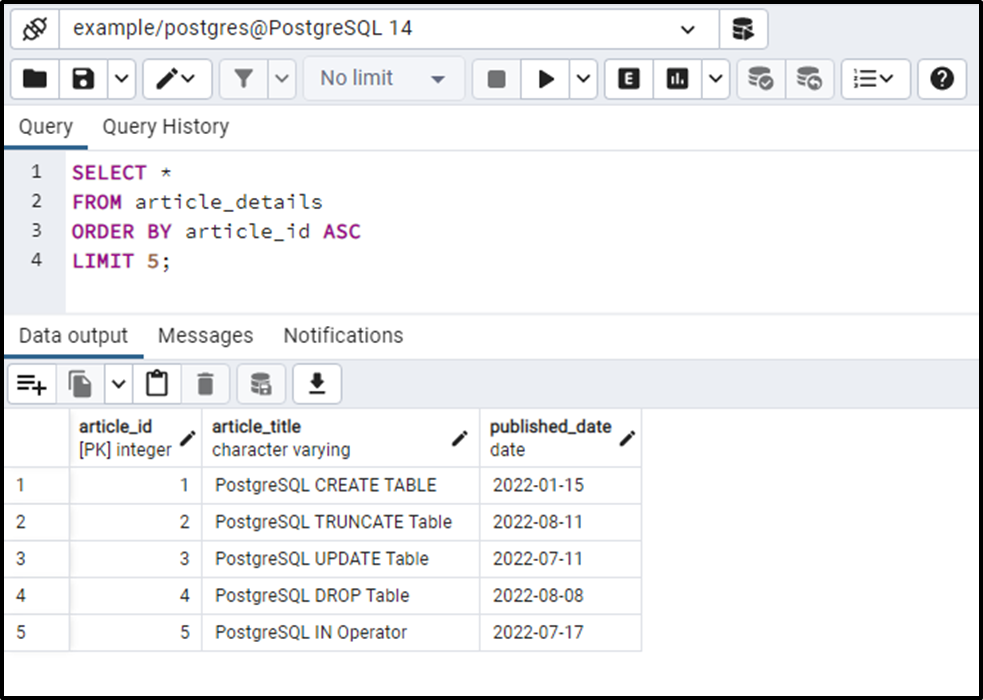
The LIMIT clause succeeded in fetching the top five records with respect to the article_id column.
Example #2: How to Fetch Top Five Recently Published Articles?
Consider the same article_details table having three columns as shown in the previous example. This time we need to fetch the top five articles concerning their published date:
SELECT * FROM article_details ORDER BY published_date DESC LIMIT 5;
Since we want to fetch the top five recently published articles, so we sorted the published_date column in descending order. Next, we utilized the LIMIT clause to specify the number of records to be fetched:
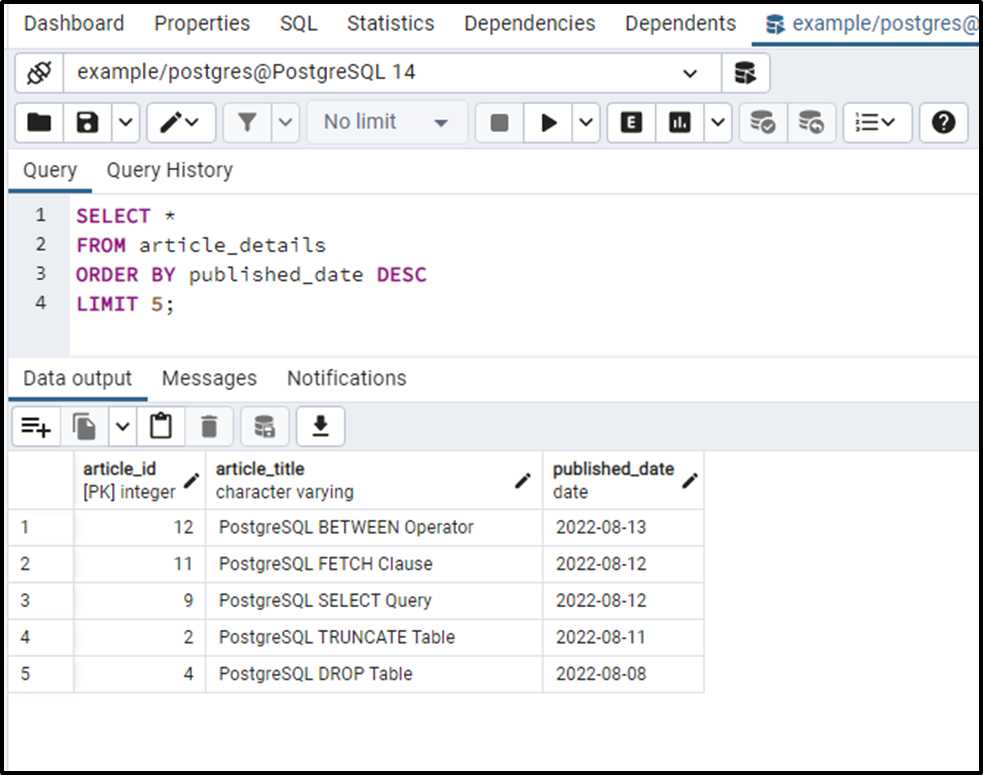
Notice that the LIMIT clause successfully fetched the top five recently published articles.
That was all the basics regarding how to get top N rows in PostgreSQL. You can get detailed information about the LIMIT clause from this article.
Conclusion
To get the top n rows of a table, the LIMIT clause is used in PostgreSQL. The LIMIT clause allows us to extract a subset of rows from a resultant table returned by a query. It is an optional clause; however, if we have to fetch the first N rows, then the LIMIT clause must be used. This article uses a couple of examples to demonstrate how to get top N rows in PostgreSQL using the LIMIT clause.



