Inserting new data to a table or deleting unnecessary data from a table are frequently performed operations in any database, including PostgreSQL. PostgreSQL provides INSERT and DELETE statements to insert or delete the records from a table. In Postgres, use the comma-separated syntax with the INSERT query to insert multiple rows into a table. And use the delete statement with an IN clause to delete multiple records from a table.
This post will teach you how to insert or delete multiple/bulk rows from a PostgreSQL table via practical examples.
How to Insert or Delete Multiple Rows in PostgreSQL
Follow the steps below to insert or delete multiple/bulk rows.
So, let’s get started with the table creation.
Create a Sample Table
Firstly, we create a sample table with multiple columns: st_id, st_name, st_department, st_age:
CREATE TABLE staff_information( st_id INT PRIMARY KEY, st_name TEXT, st_department TEXT, st_age SMALLINT );
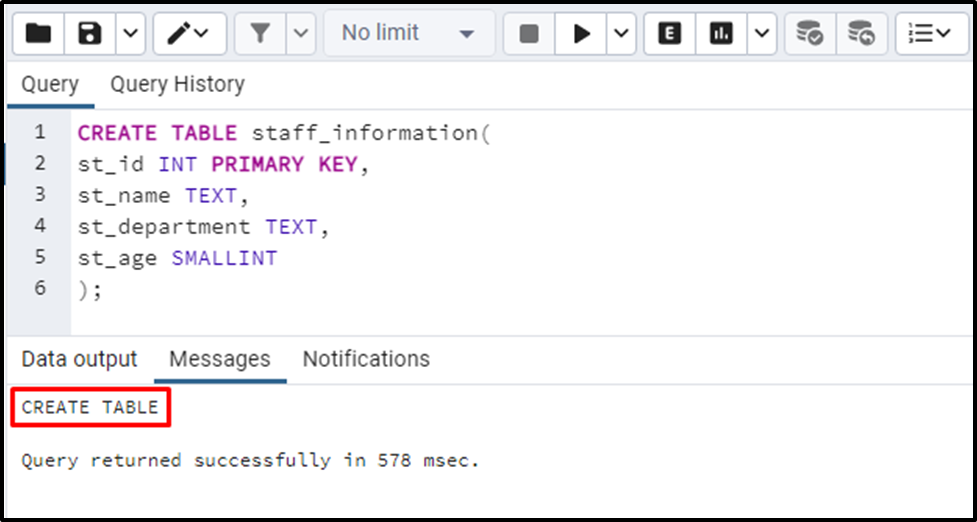
The “CREATE TABLE” message in the output window indicates that the “staff_information” table has been created. You can verify the table’s creation via the below command:
SELECT * FROM staff_information;
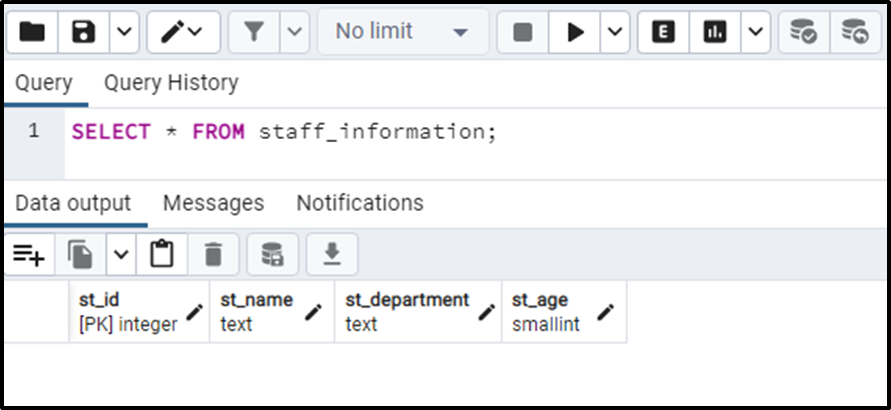
The table’s structure shows that the staff_information table has been created with four columns: st_id, st_name, st_department, and st_age.
Insert Multiple Rows
To insert multiple rows simultaneously into the staff_information table, execute the INSERT statement with comma-separated syntax as follows:
INSERT INTO staff_information(st_id, st_name, st_department, st_age) VALUES (1, 'Joe', 'Writing', 26), (2, 'Joseph', 'Graphic Designing', 25), (3, 'William', 'Graphic Designing', 27), (4, 'Natie', 'Web Development’, 26), (5, 'Joe', 'Web Development’, 26), (6, 'Stephanie', 'HR', 26);
We utilize the INSERT INTO statement to insert rows into the staff_information table. After that, we utilize the VALUES keyword with the comma-separated syntax to specify the values/rows to be inserted in the staff_information table.
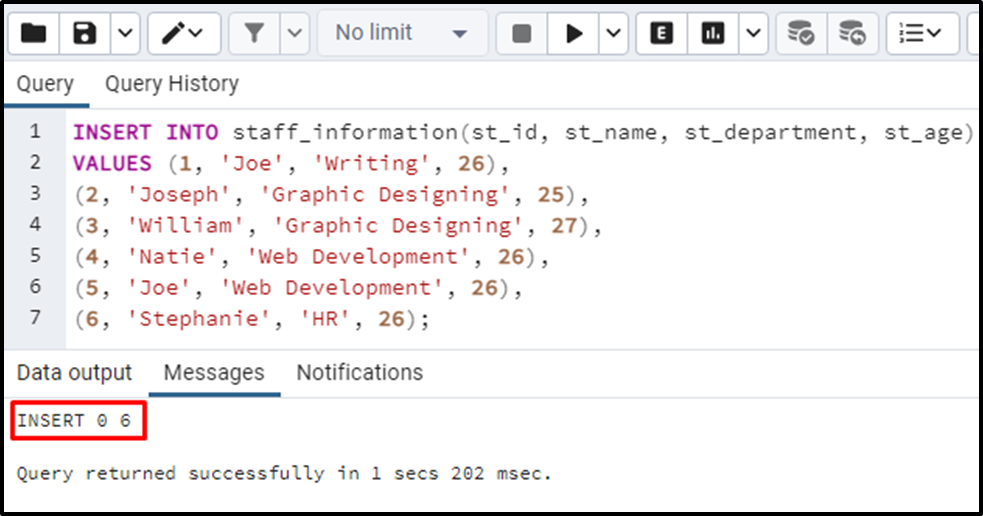
The output window shows that multiple rows have been inserted into the staff_information table. Verify the table’s data via the command:
SELECT * FROM staff_information;
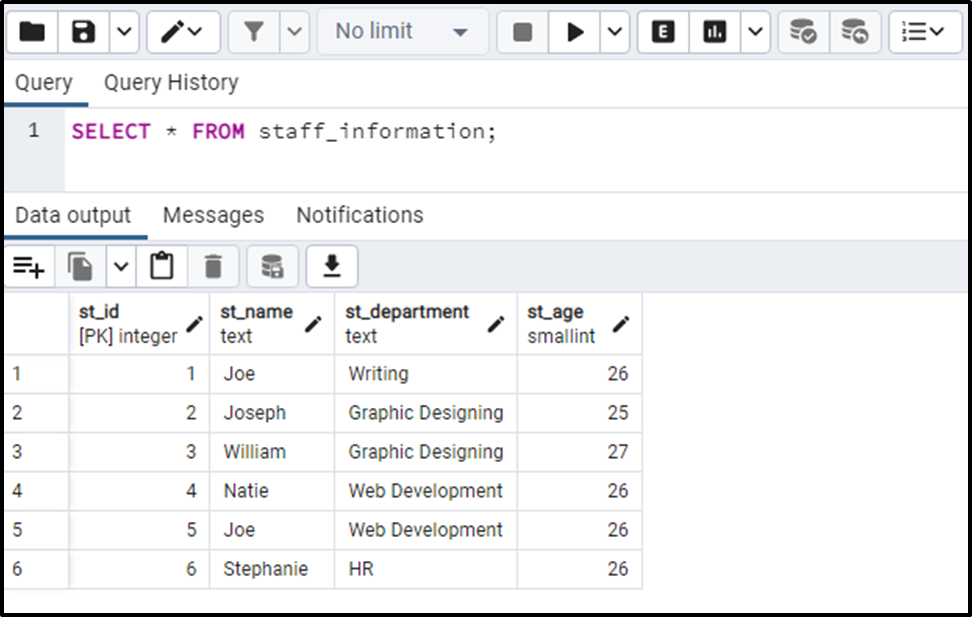
The output snippet verifies that all records have been successfully inserted into the staff_information table.
Delete Multiple Rows
Run the DELETE statement with the IN clause to delete/remove multiple rows from a Postgres table. Suppose we need to delete four rows from the staff_information table having ids “1, 3, 4, 6”:
DELETE FROM staff_information WHERE st_id IN (1, 3, 4, 6);
In the above snippet,
- We Specified the table’s name after the DELETE FROM keyword.
- Next, we specified the column’s name within the WHERE clause.
- Finally, we specified the rows to be deleted within the IN clause.
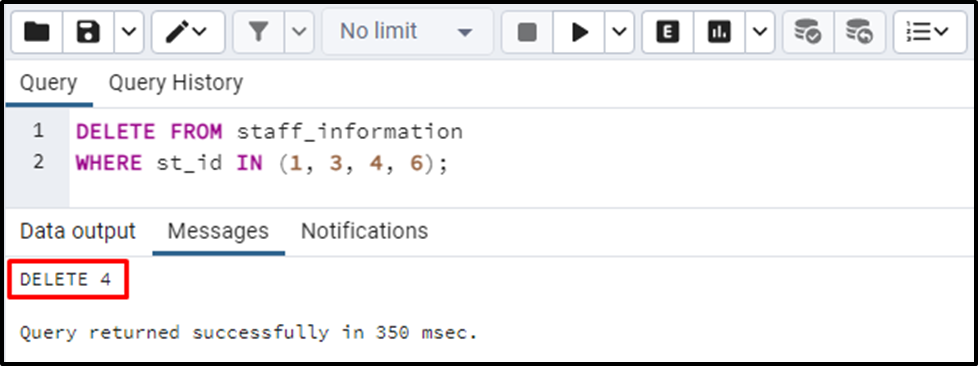
The output proves that four rows have been deleted from the staff_information table. To verify the deletion of the rows, run the below command:
SELECT * FROM staff_information;
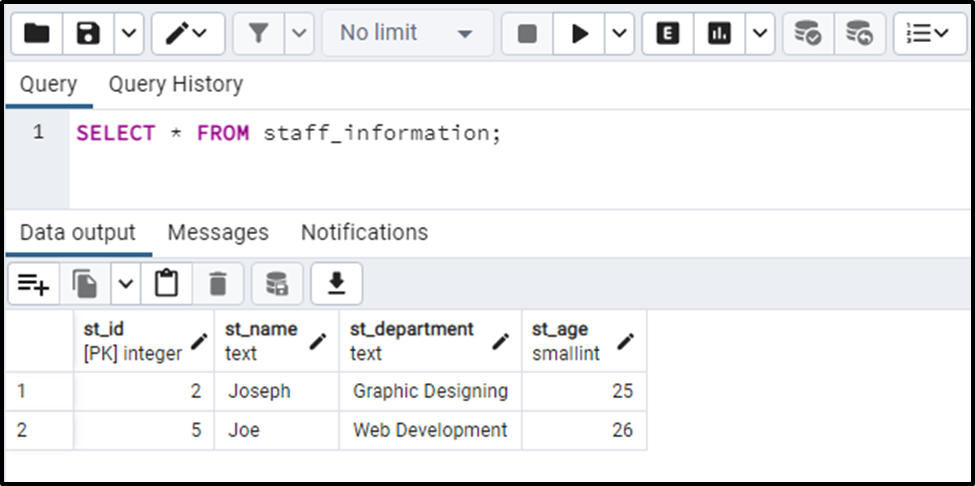
The output shows that only two rows have been left in the staff_information table, which confirms the bulk deletion.
Conclusion
PostgreSQL provides INSERT and DELETE statements to insert or delete the records from a Postgres table. In Postgres, the comma-separated syntax is used with the INSERT query to insert multiple rows into a table. The DELETE statement is used with an IN clause to delete multiple records from a table. This blog post explained how to insert or delete multiple rows from a table in PostgreSQL.



