In Postgres, TO_NUMBER() is a built-in function that converts a string/text into a number. The TO_NUMBER() function accepts two parameters, i.e., the first parameter is a “string” that needs to be converted. While the second parameter represents a “format” based on which the targeted string will be converted.
This write-up will explain the working of the TO_NUMBER function with the help of different examples. So, let’s start.
How to Use the TO_NUMBER() in PostgreSQL?
The basic syntax of the TO_NUMBER() function will be as follows:
TO_NUMBER(str, format);
Here, TO_NUMBER() is a built-in Postgres Function that requires the following parameters:
- “str” represents a string/text to be converted.
- The second parameter must be a valid format. The targeted string/text will be converted into a number according to the given format.
Here is the list of valid formats for the TO_NUMBER() function:
- “.” (dot/period) represents a decimal.
- D represents a decimal that utilizes a locale.
- 0 represents a number with leading 0’s.
- 9 represents one digit.
- Comma “,” represents a group separator.
- G represents a group separator that utilizes locale.
- RN represents a roman value between the range ‘1-3999’.
- FM(Fill mode) deletes the leading/trailing spaces.
- S represents a sign.
- SG represents the plus/minus sign.
- PL represents a plus sign for numbers greater than 0(positive numbers).
- MI represents a minus sign for the numbers less than 0(negative numbers).
- PR represents a negative value within angle brackets.
- L represents a currency symbol.
- TH/th represents the ordinal number suffix.
Now, let’s understand the working of the TO_NUMBER() function by implementing it practically.
Example #1: How to Use the TO_NUMBER Function in Postgres?
Suppose we have a string “572,7212.016-”. Let’s convert the given string into a numeric value using the following statement:
SELECT TO_NUMBER('572,7212.016-', '999G9999D999S');In the above example, “573,7212.016-” is a string that needs to be converted into a number. We utilized the “999G9999D999S” format to convert the user-specified string into a number. The stepwise description of the specified format is as follows:
- Three 9’s at the start represent that there are three digits at the start of the string.
- G at the fourth position represents that three will be a group separator “,” at the fourth position.
- The four 9’s after the G symbol represent that there are four more digits after the group separator.
- D after four 9’s represents that there will be a decimal point after four digits.
- Three 9’s after the D represent that there will be three digits after the fractional part.
- S at the end represents a sign. Since we have a negative number, we will get a minus sign.
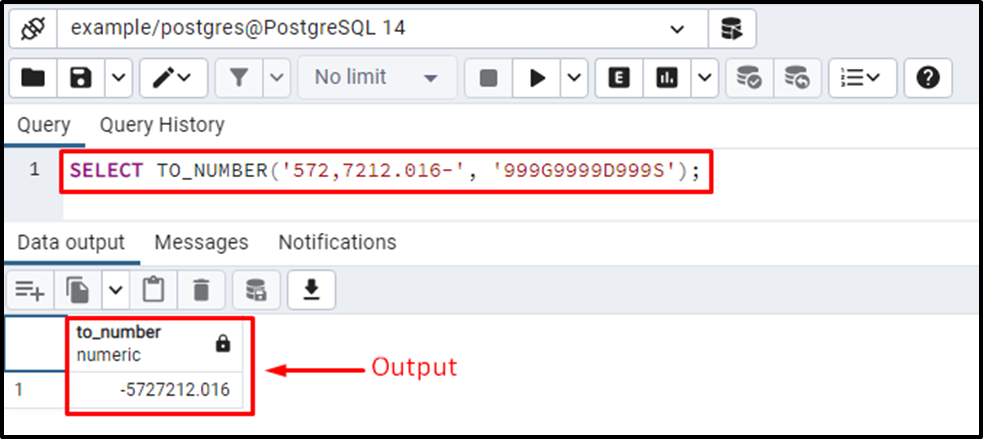
The output clarified that the TO_NUMBER function successfully converted the given string into a number.
Example #2: How to Convert a String into an Integer/Numeric Value(Skip the Floating Points)?
Suppose we have to convert a string(“572,7212.016-”) into a number, but we don’t need the decimal part of the given string:
SELECT TO_NUMBER('-512,7512.014', 'S999G9999');In this example, the TO_NUMBER() function will convert the given string (i.e., 572,7212.016-) into a number. Since we didn’t specify the D symbol and 9 in place of decimal/period and digits that come after the period. Therefore, the TO_NUMBER() function will return only the integral part and skip the fractional part.
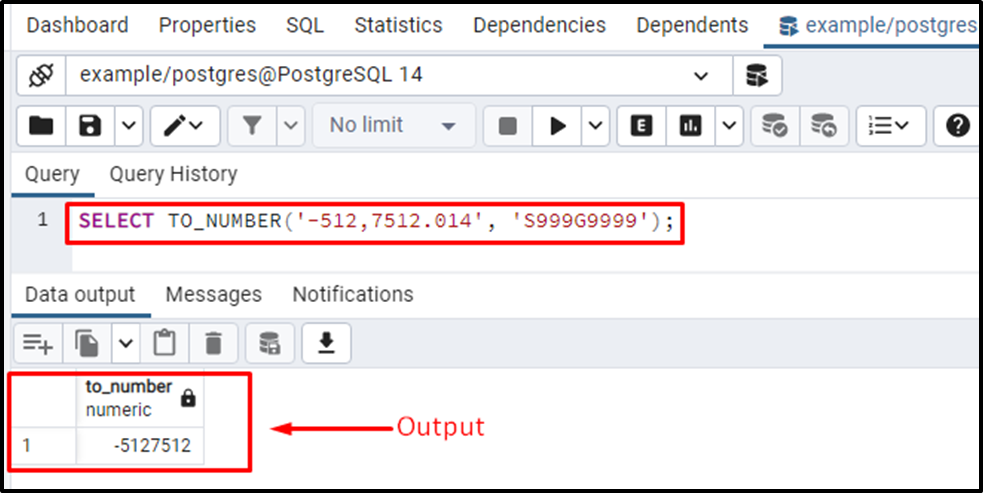
The output authenticates the working of the TO_NUMBER() function as it succeeded in converting the given string into a number.
Example #3: How to Convert a String(Cash Amount) into a Number?
Consider a string containing a special symbol (i.e., a currency symbol). Let’s utilize the TO_NUMBER() function to convert any string into a number:
SELECT TO_NUMBER('$512,7512', 'L999G9999');In the TO_NUMBER() function, the L symbol represents a currency symbol.
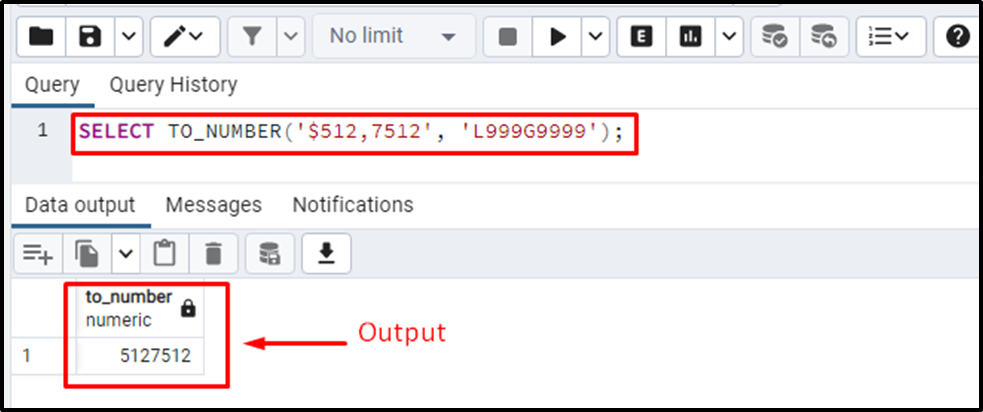
From the output, it is clear that the TO_NUMBER() function succeeded in converting the given string to a number.
Example #4: How to Convert a String(Containing Leading and Trailing Spaces) into a Number?
In the TO_NUMBER() function, the FM symbol is used to trim the leading and trailing spaces from a string. Let’s convert a string type value ‘ -1214 ' into a number type value:
SELECT TO_NUMBER(' -1214 ', 'FMS9999');In the format parameter, we specified the FM at the start that will skip the leading and trailing spaces. Next, we utilized the S symbol to specify a symbol, and at the end, four 9’s represent that there will be four digits after the (minus) sign.
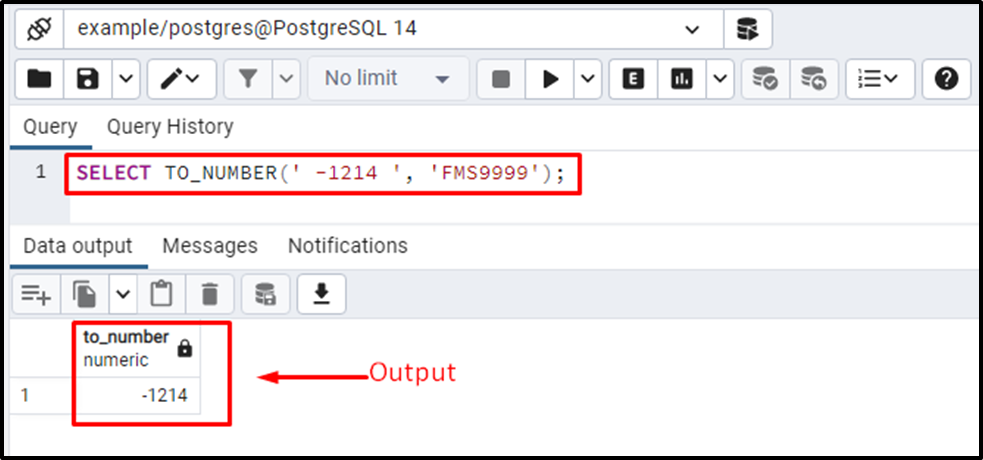
The output proves the working of the TO_NUMBER() function.
Conclusion
TO_NUMBER() is a built-in Postgres function that converts a string/text into a number. The TO_NUMBER() function accepts two parameters: the first one represents a “string” that needs to be converted. While the “format” parameter specifies the conversion criteria for the given string. There are multiple valid formats for the TO_NUMBER() function whose usage depends on the situation. This write-up explained how the TO_NUMBER() function works in PostgreSQL with the help of several examples.



