In Postgres, the ALTER VIEW statement is used to modify/alter the views’ definition. It allows us to modify the auxiliary properties of a view. Using the ALTER VIEW statement, you can set or drop the default value of a column, change the view’s owner, rename a view, etc. However, to execute the ALTER VIEW command, you must own the targeted view.
This blog illustrates several examples to showcase the usage of the Postgres ALTER VIEW statement. For this purpose, the below-mentioned topics will be covered in this blog:
- How to Rename a VIEW?
- How to Rename the VIEW’s Columns?
- How to Change the VIEW’s Owner?
- How to Set Default Value for a VIEW’s Column?
- How to Remove Default Value From a VIEW’s Column?
How to Rename a VIEW?
Let’s execute the “\dv” command to describe the list of views:
\dv;
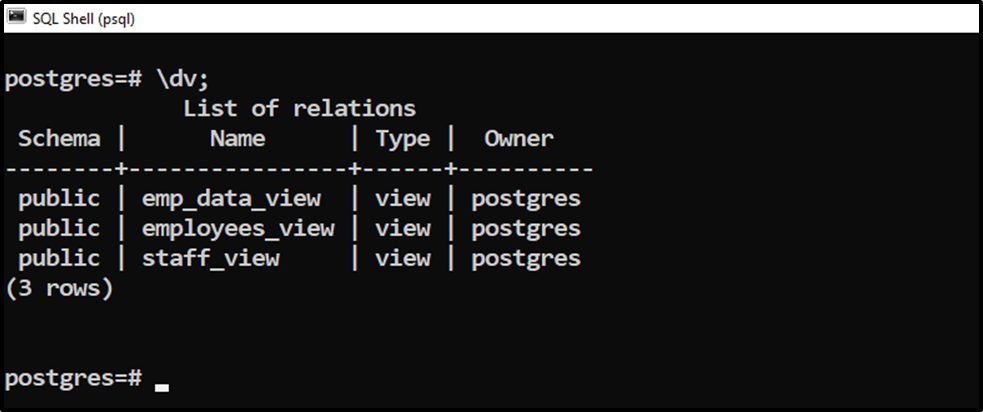
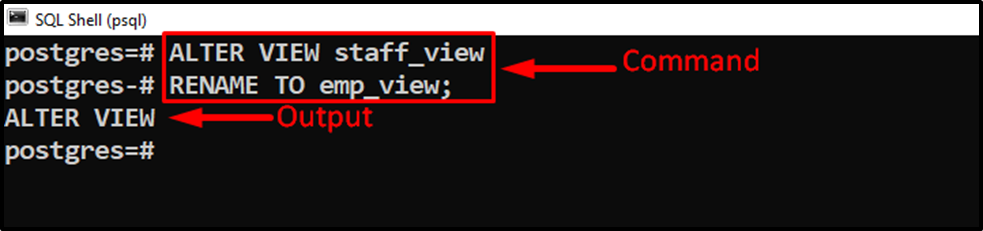
Suppose we want to rename the “staff_view” to “emp_view”. To do that, we use the “ALTER VIEW” statement as follows:
ALTER VIEW staff_view RENAME TO emp_view;
Let’s execute the “\dv” command to get the list of available views:
\dv;
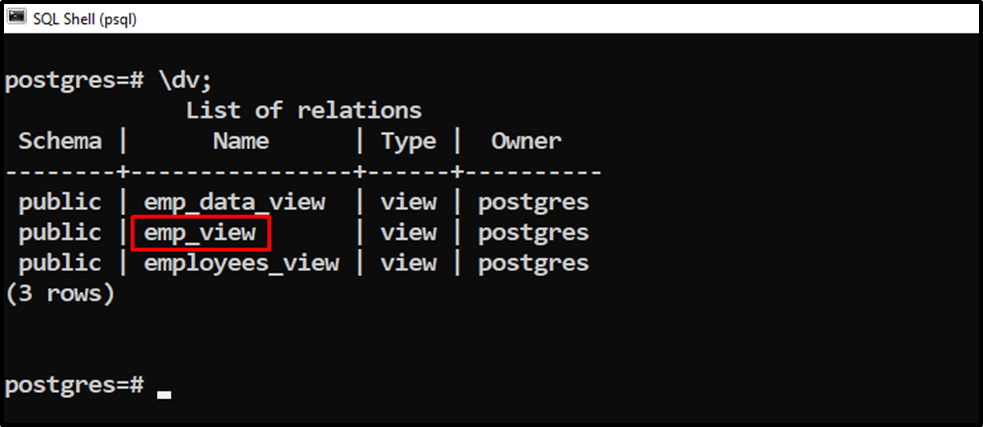
The output signifies that the “staff_view” has been renamed “emp_view”.
How to Rename the VIEW’s Columns?
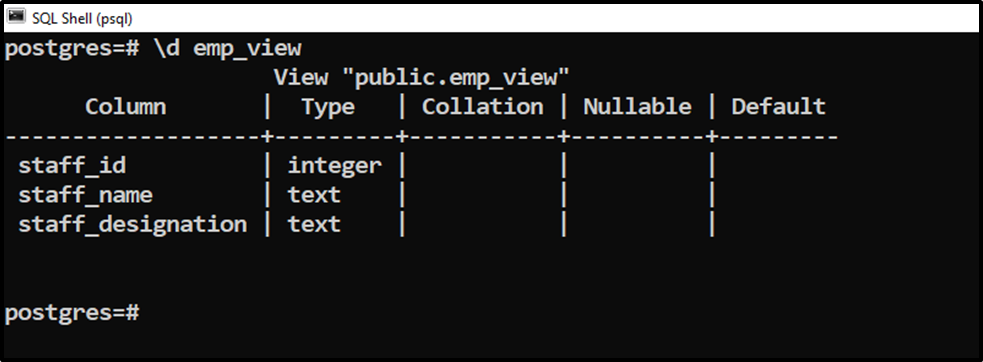
Let’s execute the “\d” command followed by the view’s name to see the view’s columns:
\d emp_view;
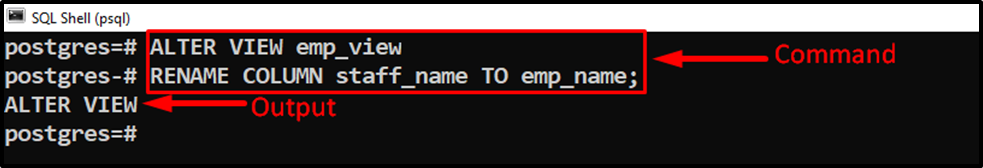
Suppose we need to rename the “staff_name” column to “emp_name”. For this, use the “ALTER VIEW” command with the “RENAME COLUMN” clause:
ALTER VIEW emp_view RENAME COLUMN staff_name TO emp_name;
Let’s check the view’s columns using the “\d” command:
\d emp_view;
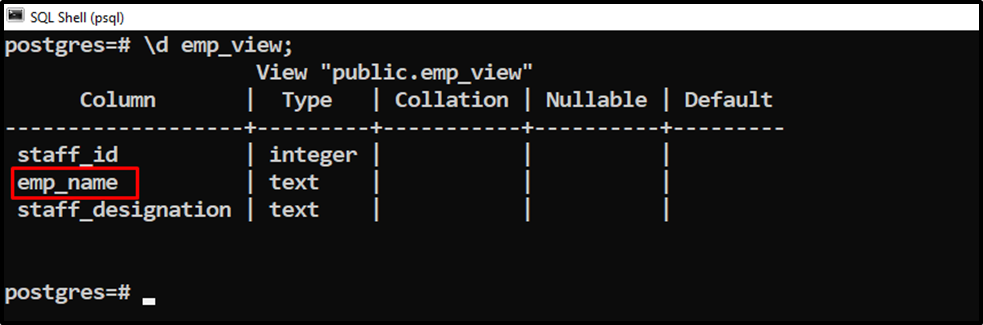
The output snippet clarifies that the “staff_name” column has been renamed “emp_name”.
How to Change the VIEW’s Owner?
Let’s execute the “\dv” command followed by the view’s name to describe the view’s details:
\dv emp_view;
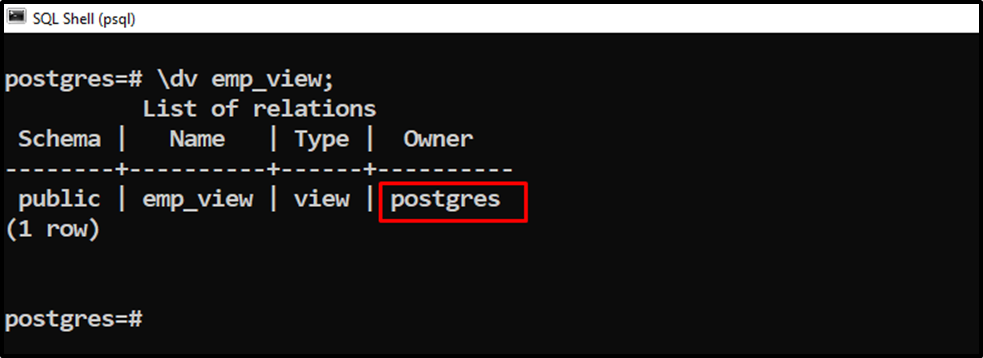
The above snippet shows that the owner of the “emp_view” is “postgres”. Let’s change it to “cp_user”:
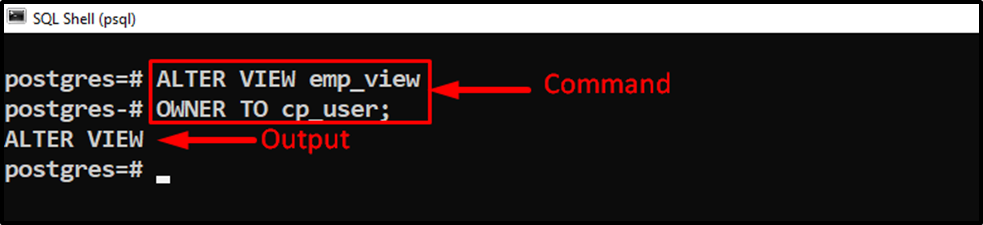
ALTER VIEW emp_view OWNER TO cp_user;
Specify the name of the user/role in place of “cp_user”:
Let’s execute the “\dv” command followed by the view’s name to check the view’s owner:
\dv emp_view;
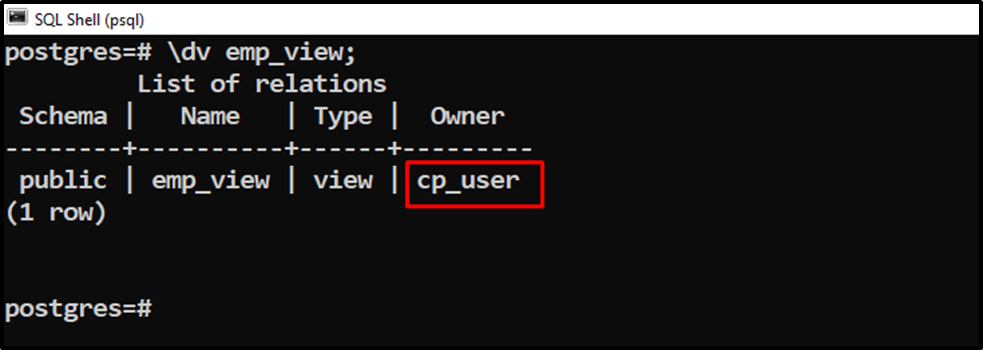
The output proves that the owner of the “emp_view” has been changed to “cp_user”.
How to Set Default Value for a VIEW’s Column?
Firstly, let’s check the view’s columns using the “\d” command:
\d emp_view;
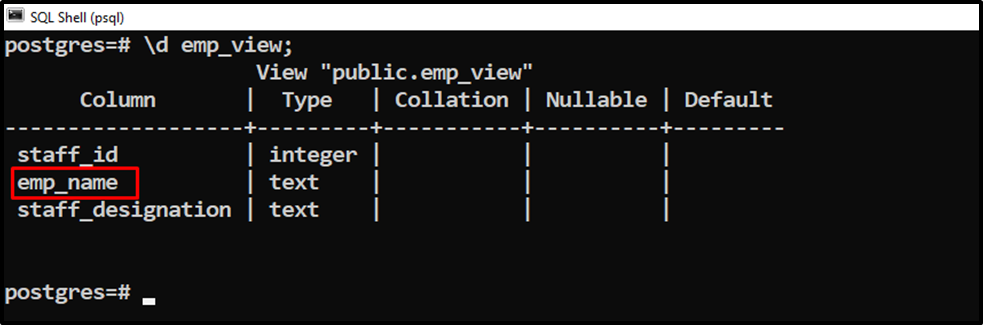
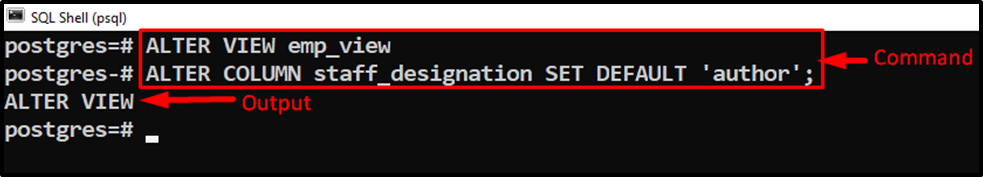
Suppose we want to set the default value of the “staff_designation” column as “author”. For this, we will use the ALTER VIEW command as follows:
ALTER VIEW emp_view ALTER COLUMN emp_designation SET DEFAULT;
Execute the “\d” command to see the columns’ definition:
\d emp_view;
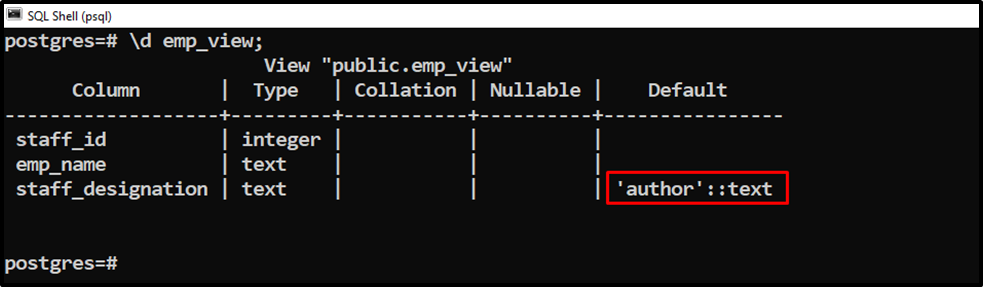
The output shows that a default value has been assigned to the “staff_designation” column.
How to Remove Default Value From a VIEW’s Column?
Use the “ALTER VIEW” and “ALTER COLUMN” commands with the “DROP DEFAULT” clause to remove a default value from a view’s column:
ALTER VIEW emp_view ALTER COLUMN staff_designation DROP DEFAULT;
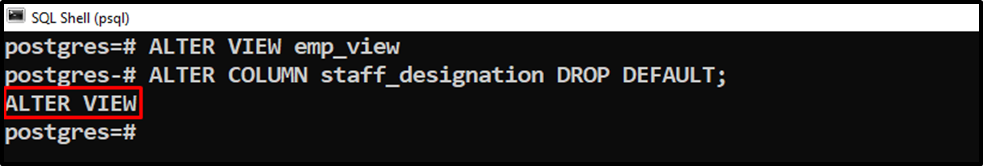
Execute the “\d” command to see the columns’ definition:
\d emp_view;
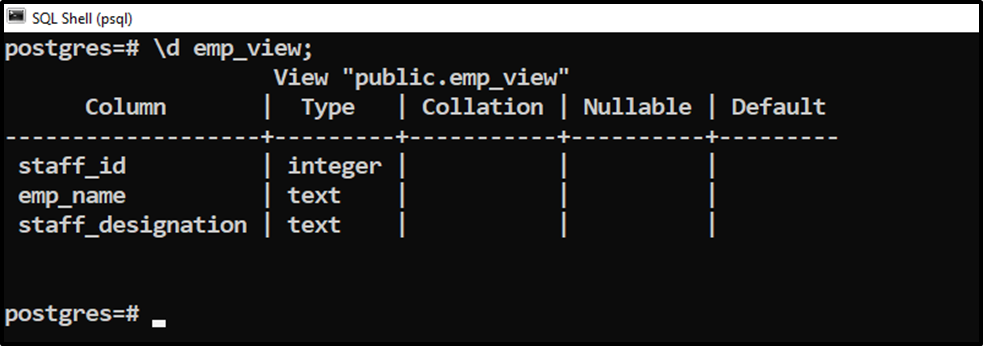
The default value has been successfully removed from the “staff_designation” column.
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, the ALTER VIEW command allows us to modify/alter the views’ definition. For instance, using the ALTER VIEW statement, you can set/drop the default value of a column, change the view’s owner, rename a view, etc. In this blog, we have demonstrated multiple examples to explain the usage of the Postgres ALTER VIEW statement.



