The SPLIT_PART() in Postgres is an incredibly useful built-in function for manipulating and extracting data from strings. The SPLIT_PART() function allows us to determine a delimiter/separator based on which the string will be divided. It can accept any character or sequence of characters, such as a comma, a space, or even a regular expression.
This post will guide you on extracting the data from a string using the SPLIT_PART() function in Postgres. So, let’s start.
PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART Function: Extracting Data From a String
The SPLIT_PART() function assists us in extracting the data from strings such as employee name, address, or any other data that contains multiple pieces of information separated by a delimiter/separator:
SPLIT_PART(str, del, position);
Here in this syntax:
The “str” represents a string to be separated/split. The “del” argument represents a delimiter/separator based on which the given string will split. While “position” specifies the substring's position, it must be a positive number.
Example 1: Split the Given String From a Comma
In the following code, we utilize the “,” as a delimiter:
SELECT SPLIT_PART('Hello, welcome, how are you', ',', 3);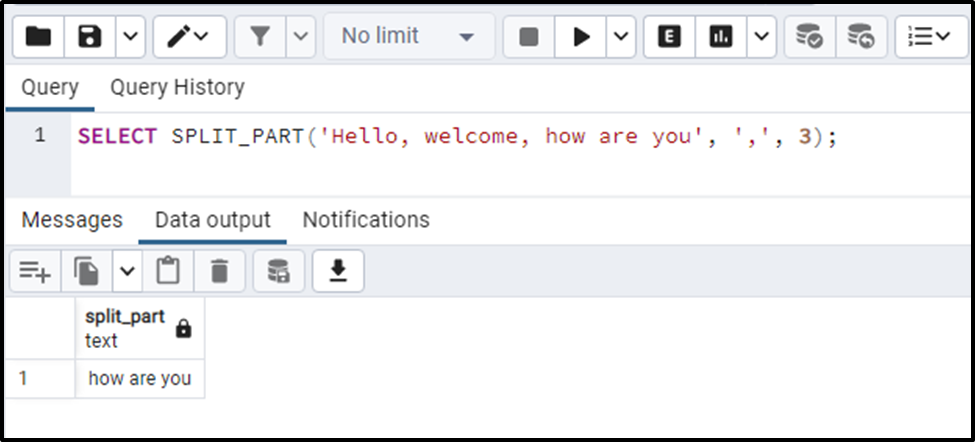
The SPLIT_PART() extracts the data from the string based on the specified position.
Example 2: Splitting Dates From Hyphen “-”
We have already created a table named articles_info, whose data is shown in the following snippet:
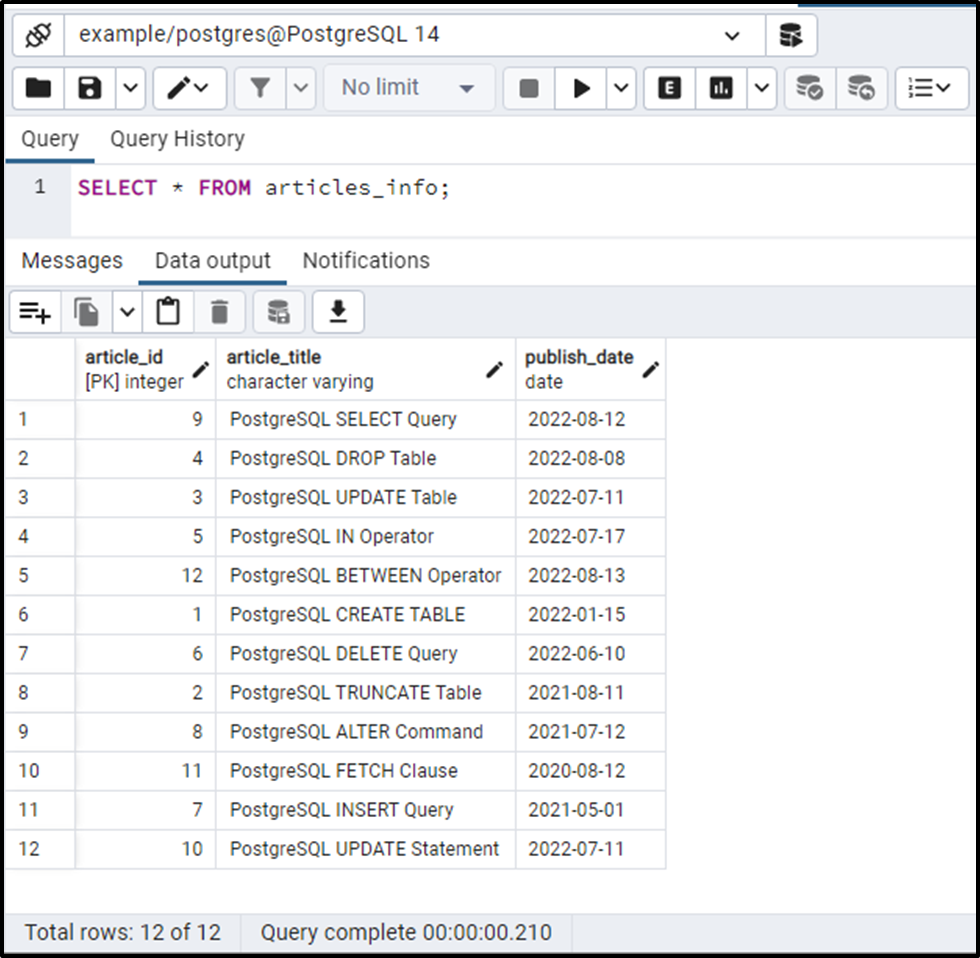
Let’s split the publish_date and retrieve the year, month, and day, separately:
SELECT article_title,SPLIT_PART(publish_date::TEXT,'-', 1) AS Year, SPLIT_PART(publish_date::TEXT,'-', 2) AS Month, SPLIT_PART(publish_date::TEXT,'-', 3) As Day FROM articles_info;
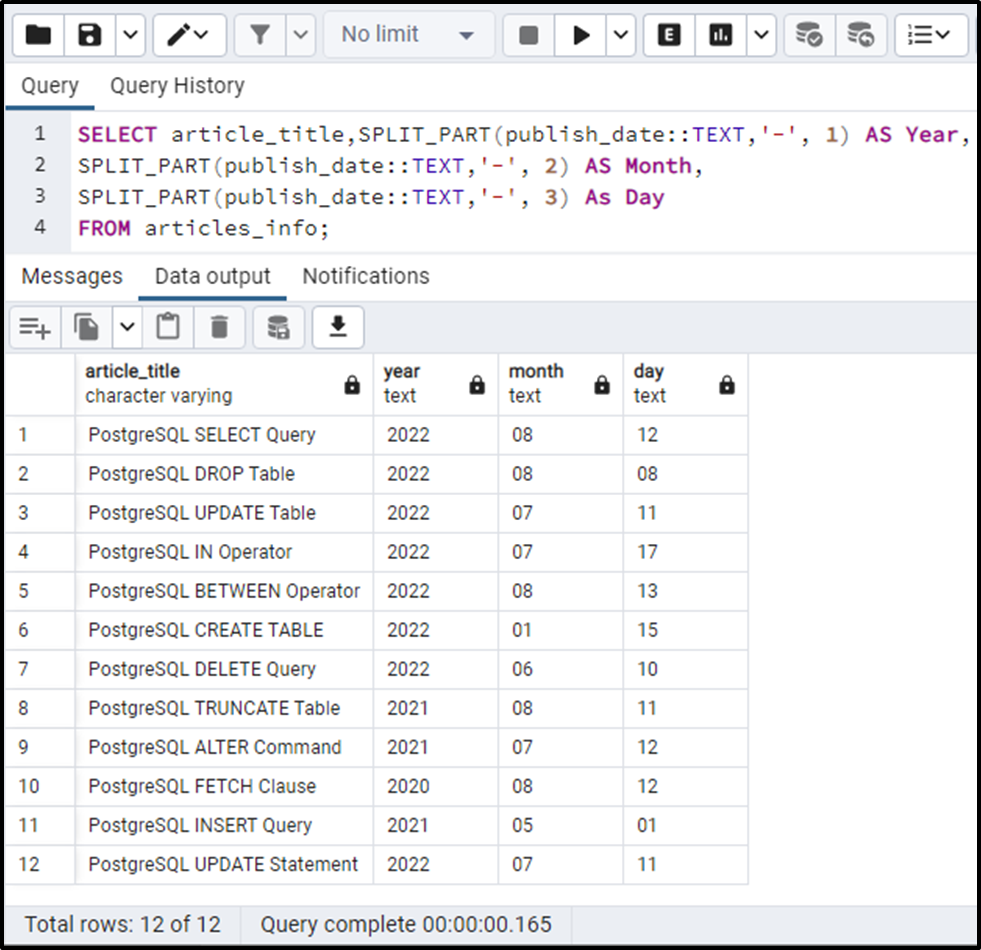
The output demonstrates that the SPLIT_PART() function extracted the published date successfully.
Example 3: Splitting Article Titles From a Space
The below statement will split the article titles from a from and retrieve the data based on position “2”:
SELECT article_title,SPLIT_PART(article_title,' ', 2) FROM articles_info;
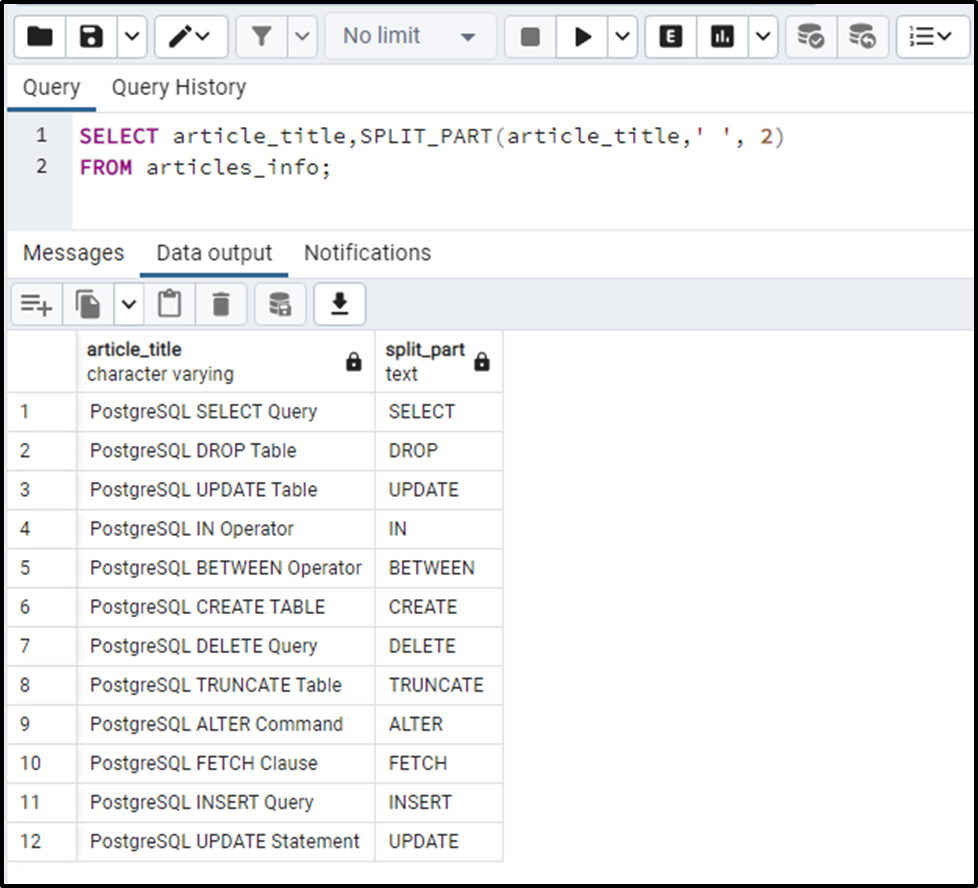
The output verifies the working of the SPLIT_PART() function.
Conclusion
The SPLIT_PART() in Postgres is a built-in function used for manipulating and extracting data from strings. The SPLIT_PART() function allows us to determine a delimiter/separator based on which the string will be extracted. It accepts three arguments: a string, a delimiter/separator, and a position. Consequently, it retrieves the extracted data from the given string. This post demonstrated the practical usage of the SPLIT_PART() function using examples.



